Why established companies fail to introduce disruptive technologies? What internal processes are holding them to do so? Asking Plant Managers, CIOs and Innovation Leaders within large companies and different sector paint a situation like this:
- They are in their confort zone and have no need to introduce them: for regulatory reasons, or due to the fact that they already eat a large portion of the cake of the business, they don´t feel the need of it
- They are not familiar with them and their internal resources are far away from this challenges: the employees are obsolete on new technologies and how to introduce them.
- They focus only in the production
- They don´t screen the market for new trends
- Disruptive Technologies go faster than their capabilities to introduce new technologies
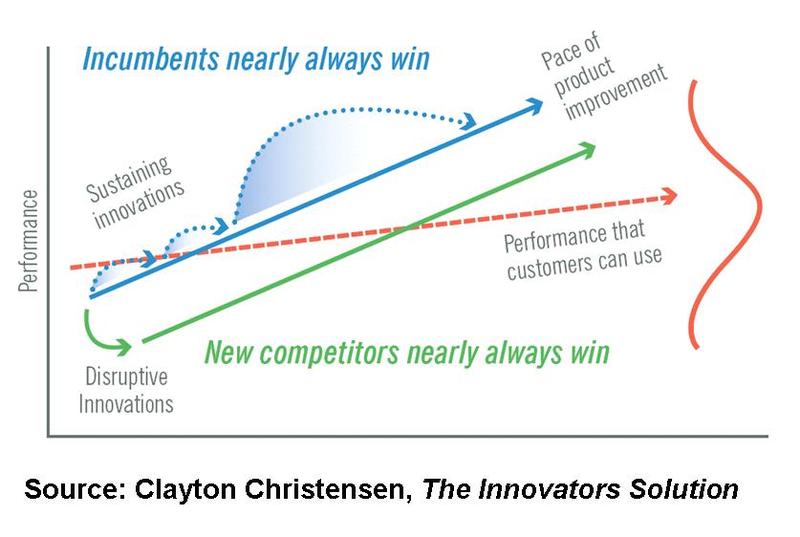
That means, established companies are excellent at developing the sustaining technologies that improve the performance of their current products in the ways that
matter to their customers. And this is because their management practices are biased towards:
matter to their customers. And this is because their management practices are biased towards:
- Listening to mainstream customers
- Investing agressively in sustaining technologies that give those customers what they say they want
- Targeting larger markets rather than smaller ones
Disruptive technologies, however, are distintly different from sustaining technologies, because:
- Disruptive Technologies change the value proposition in a market: they intend to introduce something new, upgraded or different in the market.
- When they first appear, they always offer lower performance in terms of the atributes that mainstream customers care about: the process of creating is a long term activity with many proof and error loops.
- Think of batteries or autonomous cars!
- They are ment to be cheaper: in this life, at the end of the day, everything is about money, and our quickest way to convince our Customers.
- They generaly promise lower margins, not higher profits: this is a risk that the originator of the disruptive technology must take into account. A good finantial Plan will help address the cushion of profits existing.
- Leading firms of the most profitable customers can´t use them or don´t want to use them: related to the fact that they only focus in their current existing production, they don´t screen the market for new trends.
- They are first commercialized in emerging or insignificant markets: those where big companies believe it does not deserve to pay attention.
Principles of Disruptive Technology
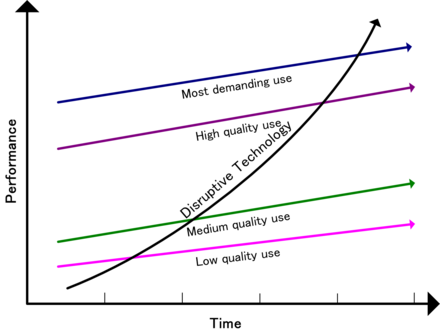
Four pillars sets the foundations of Disruptive Technology:
- Companies depend on Customers and Investors for resources: that means, if my Customers or Investors are not interested, we shall not go for that. In this regards, our value proposition to them has to come with a robust and convincing plan.
- Small markets don´t solve the growth needs of large companies: niches, they are not interested, those markets are too small for them. Example: cabrios in the automotive sector - most of the OEMs do not manufacture them any more.
- Markets that don´t exist can´t be analyzed: there are several examples related to Disruptive Technologies, such us Artificial Inteligence or Machine Learning, where many people talk about them but when you deep dive the reality is that there are only few success cases.
- Technology Supply may not equal market demand: Tech may be existing, but there is no demand for it.
Managers facing Disruptive Technologies: Actions!
- Give responsiblity for disruptive technologies to organizations whose customer need them so that resources will flow to them
- Set up a separate organization small enough to get excited with small gains:
- think of an start up ecosystem where accountablity and empowerment is given to those creative workers, offering them empowement and accountability, and everything under the umbrella of the well-established company
- Plan for failure:
- Being right the first time, this is something that unfortunately never happens.
- Learn from commercializing, and do it as soon as you have an MVP (Mininum Viable Product) / MSP (Minimum Saleable Product)
- Make revisions as you gather data, and link to the FMA (Failure Mode Avoidance) Process.
- Don´t count on breakthroughs:
- Go outside early and find the market for the current atributes of the technology.
- Outside we will find that the atributes that make disruptive technologies unattractive to mainstream markets are the atributes on which the new marketwill be build
- Applying the traditional management practices that lead to success with sustaining technologies always leads to failure with disruptive technologies.